Excessive sweating can affect confidence, comfort, and quality of life. While everyone sweats to regulate body temperature, some people experience sweating that is far beyond what is needed. This condition is known as hyperhidrosis.
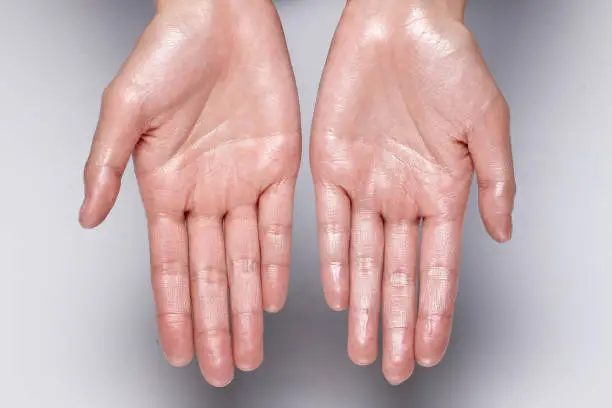
Understanding hyperhidrosis treatments: what works and what doesn’t is essential for finding relief and managing symptoms effectively.
Just as many people seek face treatments to look younger to maintain appearance, those living with hyperhidrosis explore options that can provide real and lasting improvements.
What Is Hyperhidrosis?
Primary Hyperhidrosis
Primary hyperhidrosis is caused by overactive nerves that stimulate sweat glands without being triggered by heat or exercise. It usually affects specific areas such as the hands, feet, underarms, or face.
Secondary Hyperhidrosis
Secondary hyperhidrosis is linked to medical conditions or medications. It often causes generalised sweating across the body and may occur at night.
Hyperhidrosis Treatments: What Works and What Doesn’t
Topical Antiperspirants
Antiperspirants containing aluminium chloride are often the first step. They work by blocking sweat ducts, reducing the flow of perspiration.
Effective for: mild to moderate cases. Limitations: may cause irritation, and results vary from person to person.
Prescription Medications
Oral anticholinergics such as glycopyrrolate reduce sweating by blocking nerve signals.
Effective for: generalised sweating or when other methods fail. Limitations: side effects such as dry mouth, blurred vision, and constipation make long-term use difficult.
Injection-Based Hyperhidrosis Treatments: What Works and What Doesn’t
Botulinum Toxin (Sweat Injections)
Botulinum toxin injections temporarily block the nerves that stimulate sweat glands.
Effective for: underarms, hands, and feet. Limitations: results last 4–6 months and repeat sessions are required. Some people find injections in the palms painful.
Device-Based Hyperhidrosis Treatments: What Works and What Doesn’t
Iontophoresis
This treatment involves passing a mild electrical current through water while hands or feet are submerged. It reduces sweat production by temporarily disabling sweat glands.
Effective for: palms and soles. Limitations: requires regular sessions to maintain results, which may be inconvenient for some.
Microwave Therapy
Microwave energy destroys sweat glands under the arms, providing long-term relief.
Effective for: underarm sweating. Limitations: not suitable for hands or feet. Cost can also be a barrier.
Surgical Hyperhidrosis Treatments: What Works and What Doesn’t
Endoscopic Thoracic Sympathectomy (ETS)
This surgery cuts or clamps the nerves that control sweating in the affected area.
Effective for: severe cases that don’t respond to other methods. Limitations: carries risks such as compensatory sweating in other areas, which can sometimes be more troublesome than the original problem.
Sweat Gland Removal
For underarms, sweat glands can be surgically removed or destroyed using liposuction-like techniques.
Effective for: underarm sweating only. Limitations: invasive and may not be widely available.
Natural and Lifestyle Hyperhidrosis Treatments: What Works and What Doesn’t
Dietary Adjustments
- Avoiding caffeine and spicy foods can reduce triggers.
- Staying hydrated helps regulate body temperature.
Effective for: reducing flare-ups. Limitations: does not address overactive nerves causing sweating.
Stress Management
Meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises can reduce stress-induced sweating.
Effective for: cases where anxiety is a trigger. Limitations: limited impact on primary hyperhidrosis.
Herbal Remedies
Some people try sage tea, apple cider vinegar, or herbal supplements.
Effective for: anecdotal relief in mild cases. Limitations: no strong scientific evidence to confirm effectiveness.
How to Choose Between Hyperhidrosis Treatments
Factors to Consider
- Location of sweating (hands, feet, underarms, face).
- Severity of symptoms.
- Tolerance for side effects.
- Cost and availability of treatment.
- Willingness to maintain long-term or repeat sessions.
Combining Treatments
For many people, the best outcomes come from combining methods. For example:
- Using topical antiperspirants daily.
- Scheduling botulinum toxin injections every six months.
- Practising lifestyle adjustments for added support.
Hyperhidrosis Treatments: What Works and What Doesn’t in Australia
Accessibility of Treatments
Australian clinics widely offer botulinum toxin injections, microwave therapy, and iontophoresis devices. Chemical peels and laser resurfacing (more common in cosmetic clinics) may also be used for combined care.
Sun and Climate Considerations
Hot weather makes hyperhidrosis more noticeable in Australia. This increases demand for long-lasting treatments such as microwave therapy and injections.
Risks and Safety of Hyperhidrosis Treatments
Common Side Effects
- Skin irritation from topical antiperspirants.
- Discomfort during injections.
- Temporary weakness in the hands after botulinum toxin treatment.
Rare Complications
Surgical procedures carry greater risks, including infection, nerve damage, or compensatory sweating.
Importance of Professional Guidance
Seeing a dermatologist or qualified practitioner ensures safe, effective, and tailored care.
The Emotional Impact of Hyperhidrosis
Daily Challenges
Excessive sweating affects work, social life, and confidence. Simple tasks like shaking hands or using electronic devices can become stressful.
Relief From Effective Treatments
Hyperhidrosis treatments that work give people more control and improve quality of life. While not all solutions are permanent, even partial reduction can make a significant difference.
Future Directions in Hyperhidrosis Treatments
Research on New Medications
Scientists are investigating topical anticholinergics with fewer side effects, providing hope for more convenient options.
Non-Invasive Devices
Laser-based methods and updated iontophoresis technology are being developed to offer longer-lasting results with less discomfort.
Conclusion
Hyperhidrosis treatments: what works and what doesn’t depends on individual needs, severity, and treatment goals. For mild cases, topical antiperspirants and lifestyle changes may be enough.
For moderate to severe sweating, injections, iontophoresis, or microwave therapy provide effective relief. Surgery remains a last resort due to risks.
By consulting professionals and considering both effectiveness and safety, people can find treatments that significantly reduce sweating and improve quality of life. Managing hyperhidrosis is not always simple, but with the right plan, lasting relief is possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which hyperhidrosis treatment lasts the longest?
Microwave therapy offers one of the longest-lasting results, as destroyed sweat glands do not grow back. Surgery also provides permanent effects, but side effects can limit suitability.
Are botulinum toxin injections safe?
Yes, when administered by trained professionals. Results are temporary, and treatments need to be repeated every few months.
Can lifestyle changes alone manage hyperhidrosis?
Lifestyle changes may reduce triggers but rarely eliminate symptoms entirely. Most people require medical or procedural treatments for noticeable improvement.
